📄 Grass: Decentralized Web Crawling Network¶
- 👤 Author: Jason Han
- 📆 Presentation Date: [2025-07-02]
1. Overview¶
- Project Name: Grass
- Category: Decentralized AI Infrastructure
- Key Technologies / Platforms: ZK proof, Sovereign Rollup, Reputation Scoring, Solana
- Official Links:
- Website
- Foundation
- Program Download
- Contract Address: Grass7B4RdKfBCjTKgSqnXkqjwiGvQyFbuSCUJr3XXjs (Solana)
- Whitepaper: N/A
- Docs
- GitHub: N/A
- X
- Discord
📌 Summary¶
Grass is a decentralized web crawling network that leverages the idle internet bandwidth of ordinary users to solve the problem of IP blocking during web crawling. Users install Grass Nodes on their devices to participate in crawls and receive token rewards in return. The blockchain is utilized for ZK proofs and on-chain records to ensure the integrity of the work and transparent reward distribution. In just over a year, the network has gained over 3 million users and improved network processing efficiency by 60x with the Sion upgrade. It also features a well-designed incentive structure, including a token-based point system, multi-tiered referrals, and reputation-based rewards. By combining crowdsourcing and blockchain, Grass is creating a new paradigm for AI data collection. However, it is still using blockchain for data validation and token issuance, and it remains to be seen how it will evolve key components such as the Validator and Router into a decentralized structure.
2. Background & Problem Statement¶
AI model development and data collection¶
Developing an AI model like LLM requires a huge amount of data. The process of collecting, cleaning, and tokenizing this data for training is time-consuming. While the advent of Transformers has enabled unsupervised learning without the need for labeled data, real-time web crawling is still a major challenge for learning and reasoning based on the latest information.
The State of Web Crawling¶
The web crawling market is expected to be worth $1.03 billion in 2025, with an average annual growth rate of 14%. Here are some indicators from the Web Crawling Market Report (https://thunderbit.com/blog/web-crawling-stats-and-industry-benchmarks) - 65% of enterprises worldwide have adopted web crawling or data extraction technology - E-commerce is the most active sector, with 48% of web scraping users in this space - 65% of organizations use crawled data for AI training and analytics - About 80-90% of the web is unstructured data - About half (49.6%) of web traffic is from bots - About 43% of all websites employ bot defense technologies like CAPTCHAs and Cloudflare
Web crawl prevention technologies are expanding¶
As mentioned in the previous report, 43% of sites are employing bot defense technologies. Multi-layered access controls such as Cloudflare, CAPTCHAs, IP restrictions, and JavaScript-based rendering are becoming more common, and common crawling tools (e.g., Python's requests, scrapy) are being blocked by many sites. In particular, data center IP addresses are often blocked from websites.
Web Crawling Companies¶
| Company Name | Headquarters | Features / Main Services |
|---|---|---|
| Bright Data (formerly Luminati) | Israel | Largest. Proxy+Crawl API. Supports tons of targeted websites |
| ScrapingBee | France | Headless browser-based crawling API. JS rendering available |
| Zyte (formerly Scrapy Cloud / Scrapinghub) | Ireland | Based on Scrapy open source. Crawl-as-a-service |
| Oxylabs | Lithuania | Large proxy network + enterprise data collection solutions |
| SerpApi | USA | Specializes in crawling Google search results. Captcha bypass built-in |
| Diffbot | United States | AI-powered web structure analysis → JSON data extraction |
| Webz.io | Israel | Special purpose crawling, including dark web and open web monitoring |
Here's how they crawl data. Most of them are using a centralized method to bypass web anti-crawling technologies.
| How-To's | Explained |
|---|---|
| Use Proxy Networks | Tap into millions of proxy IPs to evade IP blocks |
| Headless Browsers | Render JS with Puppeteer, Playwright, and more |
| Bypass Captchas | Automatically solve captchas or integrate with human input services |
| AI-Powered Parsing | Automatically extract key content with AI, even when the DOM structure changes |
| API Wrapping | Parse search results, news, shopping pages, and more like REST APIs |
3. How It Works¶
🔍 3.1 Project Approach¶
Grass builds a decentralized web crawling network. It crawls the web by installing web crawling nodes on the computers or phones of ordinary users. Participants provide idle internet bandwidth and Grass provides tokens as a reward. Because the participant nodes have residential IPs, they are recognized as regular users and can crawl without being IP-blocked. The unstructured data collected from nodes around the world is transformed into structured datasets suitable for AI training.
According to a January 2025 article, Grass has grown rapidly in just one year.
| Item | Numbers/Description |
|---|---|
| Number of Users (2024) | 200K → 3M (15× increase) |
| Video Indexing Scale | 1000× increase |
| Total Tokens Distributed | $196M / 2.2M+ users |
| Network Efficiency Improvement | 60× improvement with Sion Phase 1 |
| Token Price | Up about 2.5% immediately after the announcement, to a level of $2.82 |
🏗️ 3.2 Architecture¶

The Grass architecture consists of a hierarchy of Validator, Router, Grass Node, Zk Processor, Data Ledger, and Edge Embedding Models. Among them, Validator, Router, and Grass Node participate in crawling, while the rest perform data attestation and preprocessing.
- Validator
- Initiates web requests, validates transactions on nodes, and generates ZK proofs.
- Initially a single structure, but will transition to a decentralized committee in the future
- Router
- Relays requests between Grass Nodes and Validators and manages bandwidth
- Compensated based on throughput
- Grass Node
- Runs on user devices and collects web data
- Processes encryption requests, returns traffic to the router, and is rewarded based on reputation score
- Zk Processor
- Creates a ZK proof of every session and submits it to a Layer-1 blockchain (Solana)
- Web crawl history is recorded as immutable proofs
- Grass Data Ledger
- Immutable data store that links processed data with on-chain proofs
- Edge Embedding Models
- Pre-processes collected unstructured web data and refines it into a format suitable for AI training
🎯 3.3 Core Components¶
Validator¶
- One of the core roles of the network, fulfilling two main roles: initiating web requests and validating transactions
- Uses any of a variety of encryption algorithms (AEAD, RSA, ChaCha20, etc.) with its own keys for TLS connections
- Securely manages pre-master, master, and session keys on a per-session basis, which are used to evaluate the quality of node traffic
- Once validated, session data is passed to the ZK Processor for batch processing for proof generation and on-chain recording.
- Currently a single entity, but in the long term they plan to move to a structure with multiple validators with economic collateral
Router¶
- Geographically distributed hubs that relay connectivity between Grass Nodes and Validators
- Forward and manage all incoming and outgoing web requests to the Validator, while maintaining connectivity across the network
- Report metrics to the Validator, such as the size of each request/response in bytes, latency between the node and the Validator, and connection health
- Receive rewards proportional to the amount of tokens staked
- Responsible for validating the reliability and maintaining the health of nodes connected to the network
- Failure to meet the 75% or more connectivity requirement may result in a portion of staked assets being deducted as a penalty (slashing)
Grass Node¶
- Node operators offer their idle internet bandwidth and are rewarded with tokens for the traffic they generate
- Responses received from public websites are encrypted and forwarded back to the router
- Simple to install, automatically enrolls in the network once connected, and is up and running 24 hours a day
- Nodes do not have access to your personal data
- Only relays public website traffic, no personal data is processed
- Reputation Score is important to earn token rewards on the network
| Metrics | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Completeness | assesses how complete the data is |
| Consistency | assesses whether the data is consistent over time and across requests |
| Timeliness | assesses whether it is kept up to date |
| Availability | assesses how sustainable the response is |
🔁 3.4 Workflow Overview¶

- Forward the client's crawl request to the Grass Node.
- A client encrypts the crawl request and forwards it to the validator
- Validator validates the request and forwards it to the appropriate Router
- Router routes the request to the appropriate Grass Node
- Collection of web requests and responses by Grass Node
- Node de-encrypts the received encrypted request to access the actual website
- Receives the response (data/HTML) from the website
- Node encrypts the received response and forwards it to Validator via Router
- ZK Processor → Layer-1 Blockchain
- When a certain number of web sessions are gathered, ZK Processor aggregates session data
- Generates Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZK proof) using ZK technology
- The generated proof is submitted to a Layer-1 blockchain (e.g. Solana) to prove session integrity
- Data Preprocessing and Storage
- Web content and proofs are connected to the Grass Data Ledger and stored in an immutable structure
- Edge Embedding Models structure, cleanse the data and convert it into a format for AI learning
4. Token Economy (if applicable)¶
Funding & TGE(Token Generation Event)¶
The company raised $3.5M in a Seed Round in December 2023, received Series A funding in September 2024, and conducted a TGE in October. The listing price was $0.87 and is currently $0.97. Investors are listed below

Grass Token Status¶
Below is the GRASS token status on Coinmarketcap. The total token supply will be 1 billion tokens, with a current circulating supply of 240 million tokens. Each token is priced at $0.97 and has a market capitalization of $237M, currently ranking 165th on Coinmarketcap. (If all tokens were issued (1 billion), the market capitalization would be $972M (FDV, Fully-Diluted Value).

GRASS Token Supply¶
The distribution plan for 1 billion tokens is shown in the diagram below.

Currently, 240 million tokens have been issued, and will be supplied and distributed over time to reach a total supply of 1 billion tokens. The supply/distribution schedule is as follows

Grass Airdrop One¶
Token airdrops are commonly used to attract early users to a service. In the case of Grass, 100 million tokens (10% of the total supply) were airdropped to early contributors. They divided the airdrop period into 9 epochs and divided the tiers according to the number of Grass Points earned in each epoch and distributed them differently in each tier.


Grass Points¶
You don't get Grass tokens just for providing internet bandwidth. You earn Grass points, and at the end of the Epoch, tokens are distributed based on the number of points you've accumulated. The duration of an Epoch is fixed, but the number of tokens distributed per Epoch is not.
You can earn points by 1) providing internet bandwidth, or 2) inviting others to join. If you refer others, you will receive 20% of the points earned by the first referrer (Primary Referrals), and if they refer others again (Secondary Referrals), you will receive 10% of the points earned by the new referrer. You then receive 5% of the third-level invitee's points. These referral points continue to be earned as long as the referrer remains on the service.
Based on the number of referrals and points accumulated, you'll be placed in one of 10 tiers, from Iron to Titan, and receive bonus points accordingly.
Grass Staking¶
The Grass tokens you receive can be staked on the Router to earn interest. Below is the staking screen, and you can see that you'll be rewarded with an APR (Annual Percentage Rate) of 35%. This is very high compared to other staking services, and it's worth exploring how this is possible. Rewards are given in Grass tokens, but where do these tokens come from? Since there is no inflation in the token economy, we can speculate that a portion of the total supply to be issued is being paid out as rewards. Since it's early in the service, it seems to be a strategy to promote people to stake Grass tokens at a high APR to reduce the circulating supply and defend the price. However, once enough tokens are staked, the reward is expected to be lowered.

5. Project Status & Plan¶
Grass Dashboard¶
Grass provides a dashboard to view the status of the Grass network. Over 800 TB of data is collected per day.



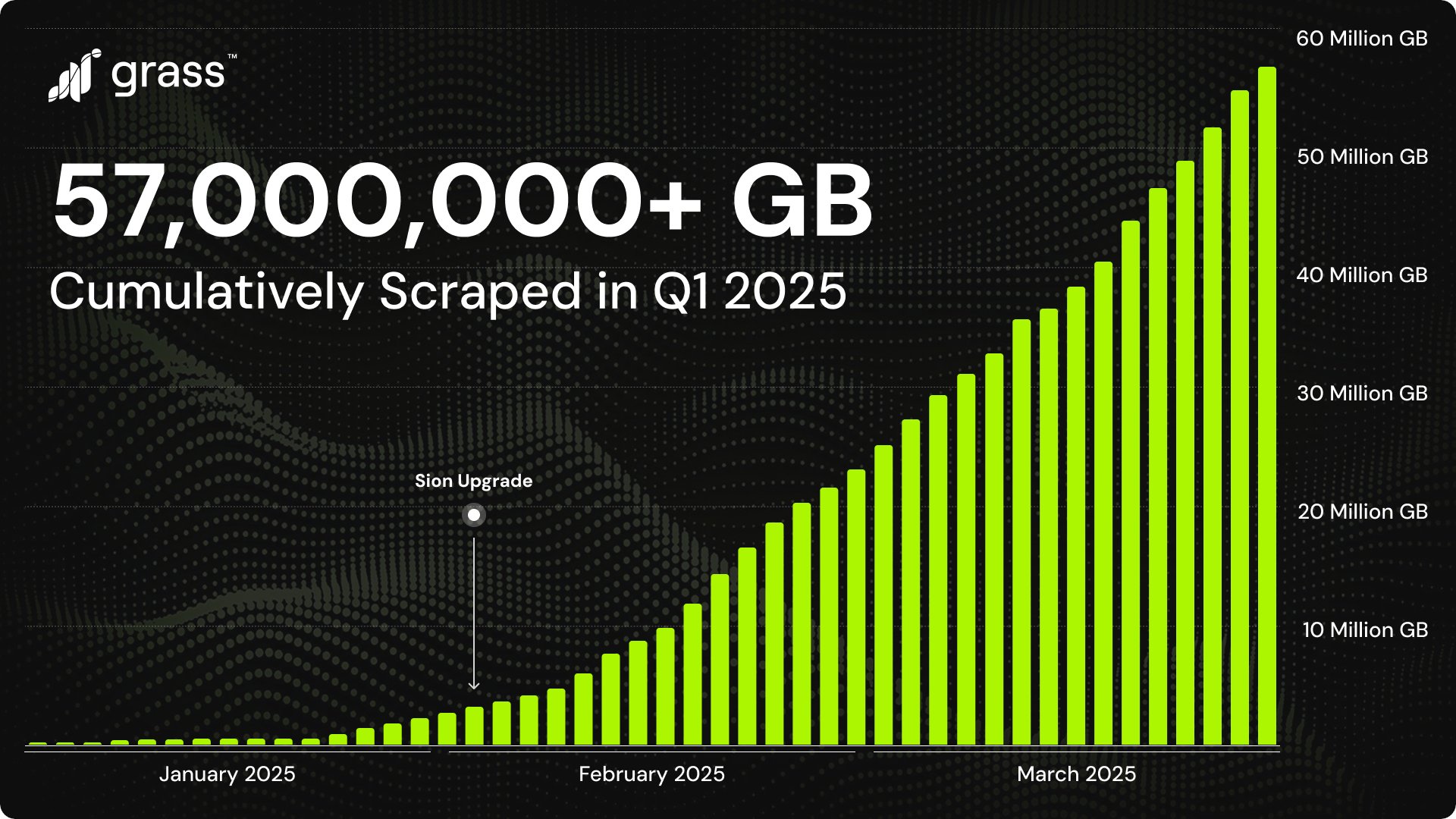
Sion Upgrade¶
February 25, 2015 Sion Phase 2 upgrade horizontally scales computing resources, improves network throughput by 10x, and supports real-time multimodal data scraping (e.g., 4K video data) at petabyte scale. The technical key is to increase throughput and speed up scraping by optimizing the scraping algorithm and distributing the workload across multiple nodes for parallel processing. This makes it possible to collect and process multimodal data that requires large-scale processing and feed data into multimodal AI development.
Grasshopper - the hardware for Grass¶

They'll be releasing Grass Node hardware soon. You don't need to set up your device, just connect it to the network and it will act as a Grass Node and earn points. It's kind of like a Grass miner.
6. User Experience & Hands-on Review (if applicable)¶
Grass Node User Interface¶
After downloading Grass Node and installing it, you can see the simple Node program UI as shown below. It shows a button to connect to the network and the points earned.

Node program UI is simple. For more information, you can look at the website dashboard instead. You can see your daily earnings statistics, a history of the networks you've connected to, your referral program status and tier, and your rewards.



Wallet and email verification process¶
The verification process takes place in three steps. 1. email verification 1. wallet verification (Solana wallet) 1. verify wallet from email (verify who the address is associated with)


Reviews¶
- Very easy to install and run
- The dashboard is intuitive and easy to use
- I feel like they care and focus on the referral program in particular
- Easy to go through the certification process
7. Why Blockchain¶
The official documentation describes the need for blockchain as follows.
-
Transactional Efficiency: Global settlement in over 190 countries is both easier and better on-chain than it is off-chain.
With participants scattered across the globe and small amounts to be paid to them, using traditional money transfer systems is not only inefficient, it's impossible.
-
Transparency: Proofs of each transaction being posted on-chain provides empirical evidence that rewards are being equitably distributed. It also provides transparency with respect to the verification of data provenance.
On-chain is the best way to ensure that everyone can verify that the distribution of tokens based on contributions is fair. And to verify the source and path of data, it should be transparently recorded on-chain.
-
User Ownership: Users should own their contributions to the internet, otherwise they will continue to be exploited by large tech companies.
In a typical big tech company, users don't know about their contributions, can't claim them, and can't be compensated for them. However, your contributions should belong to you. This requires a blockchain-based way to record and control contributions.
8. Insights & Limitations¶
✅ Key Takeaways¶
- A clever solution to the problem of IP blocking in web crawling by crowdsourcing the devices of ordinary users.
- Crowdsourcing idle device resources is an old idea. Projects like SETI@Home and Folding@Home have utilized idle resources, and software like BOINC is often used. These projects are called Volunteer Computing because people participate voluntarily without compensation. Grass, on the other hand, is used for the commercial purpose of web crawling and incentivizes participation by rewarding participants with Grass tokens.
- For crowdsourcing, where nodes are scattered around the world, tokens are the most appropriate way to reward them. Traditional fiat money transfers would be nearly impossible to implement. It is difficult to implement because you need to verify the customer and adapt to each country's financial system. In this sense, a reward system using tokens is the right choice.
- The design of the token economy is interesting. Instead of giving out tokens right away, it first gives out Grass Points and then settles and gives out tokens at the end of an Epoch. This two-step process has great advantages. First, users don't know how many tokens they will receive with their points, so it's hard to calculate the exact value of the reward, so they can postpone deciding if the reward is appropriate. And by allocating a certain amount of tokens per epoch, the demand for tokens can be fixed even if the number of participating nodes fluctuates. Also, points can be recorded off-chain, so you don't have to pay on-chain fees.
- The referral program and tier structure is a great example of gamification done right. It's a multi-tiered reward structure. They have different tiers of rewards based on referrals and the amount of points you earn, which encourages you to participate more.
- It uses blockchain as a trust engine to record proof that the crawl was performed error-free. This is exactly the kind of design that plays to the strengths of blockchain. ZK technology is used to ensure privacy, batch processing is adopted for cost efficiency, and the provenance of the data is recorded on the blockchain so that AI model developers can verify the source of the training data, which increases the trustworthiness of the data. In the future, we expect to see more similar uses of blockchain for data provenance and usage history.
⚠ Limitations / Open Questions¶
- There is no mention or evidence that Validators and Routers are yet decentralized. Although they are decentralized in terms of using people's idle network resources, the operating systems (Validator and Router) seem to be still centralized.
- In order to eliminate the operating entity, the Validator and Router must eventually be decentralized, and the ZK Processor and Data Ledger must also be decentralized. With so many decentralization points, it's hard to see how you can decentralize everything. Especially in the case of Data Ledger, it is a very difficult issue because if the amount of data stored is large, it becomes the same as decentralized storage. It remains to be seen in what direction they will decentralize in the future.
- Node Reputation Scoring is an important factor because nodes can be operated maliciously to maximize rewards. However, the documentation only states the policy to evaluate the reputation of a node, but not how to measure it. For example, it is unclear how the completeness of the response data will be measured. This is the most difficult part of crowdsourcing data collection. There needs to be some way to verify that malicious nodes are not tampering with the data or responding with fake data.
- Paying points is a clever policy to avoid tying the reward to a cash value, but the fact that the reward can fluctuate depending on the epoch is a pain point for users. If an Epoch ends and the tokens you're rewarded with don't meet your expectations, you may decide to stop participating. Also, since the price of tokens fluctuates, even if you receive the same amount of tokens, if the price of tokens drops, the real value of the tokens drops as well, and there is less incentive to stay engaged.
- One idea is to handle some scientific calculations or web crawls for public purposes alongside commercial web crawls, so that users can get the satisfaction of knowing that their resources are also contributing to a public cause.
9. Reflections & Discussion¶
💡 Personal Reflections¶
- I think the crowdsourcing approach to data collection for AI training is appropriate. Rewarding contributions with tokens is also an appropriate choice. The use of blockchain to issue and distribute tokens is understandable, but the use of blockchain to prove the integrity of web crawling and prove data provenance is less convincing. Blockchain doesn't solve the problem of how to trust an off-chain verification when the verification itself is done off-chain and only the resulting proof is recorded on the blockchain. It is the role of the blockchain to ensure that the proof is not tampered with.
- At this stage, the level of decentralization is not high, which is why blockchain is being used in a limited way. If this part can be more advanced and made into a protocol for data collection, processing, and distribution, it will have a great impact.
- It may not be sensitive to the value of the reward because it is monetized by using idle bandwidth, but it can still be affected by the price of the Grass token. It would be helpful to think of a way to hedge this part.
- In terms of organizing the AI infrastructure, we can think of various ways to apply crowdsourcing.
❓ Discussion Questions¶
- Grass mentioned they don't access personal data, but are you comfortable running Grass Node on your personal device?
- Depending on the price of the token and the number of participating nodes, rewards can be volatile, how sensitive are you to volatility?
- Besides referrals and gamification, what are other ways to drive engagement?
- What are some ways to decentralize key components like Validators and Routers?
- What other resources can we leverage for AI infrastructure besides idle internet bandwidth?